If you’re active online, then we guarantee you know what a chatbot is.
According to a study, 1.4 billion people use chatbots regularly. Although this might not seem like a large number compared to other communication methods, it’s still significant, and, more importantly, it’s growing.
In today’s digitally driven world, businesses can no longer rely on traditional service methods to satisfy their customers. Technological advances are paving the way for a new customer experience, and chatbots are at the helm.
If you’re curious about what chatbots are and how they work, you’re in the right place.
In this ultimate guide, we’ll cover:
- Chatbot Fundamentals
- Types of Chatbot Technology
- What is an AI chatbot platform?
- Chatbot Limitations
- Chatbots vs Live Chat
- Best AI Chatbot Features
- The Value of AI Chatbots for Business
- AI Chatbots for Customer Experience
- Chatbot Examples, Use Cases, and Case Studies
- Chatbot Statistics
- Chatbots and Covid-19
- The Future of Chatbots
Chatbot Fundamentals
What is a chatbot?
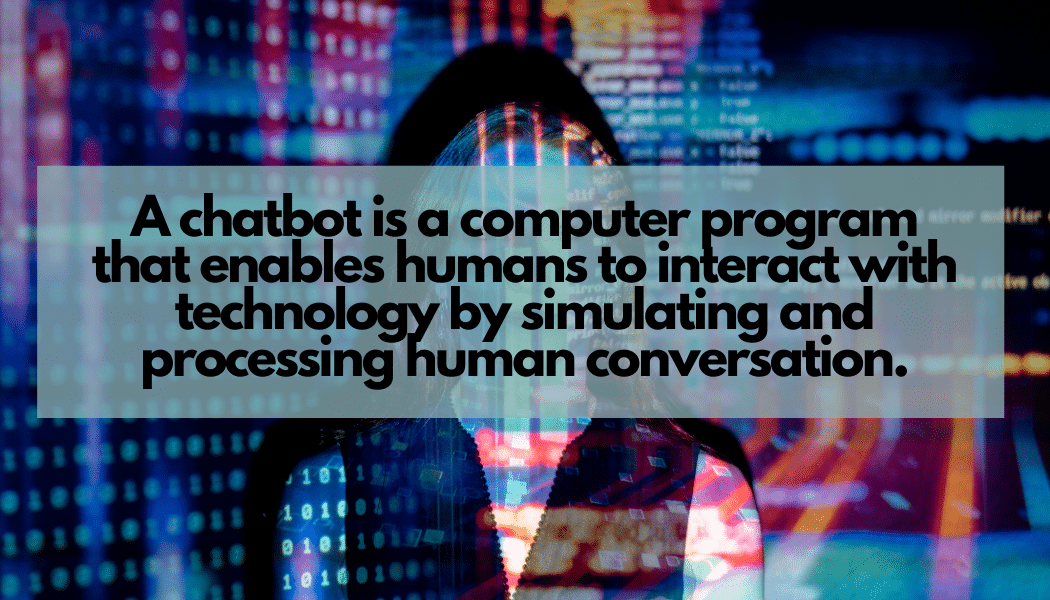
A chatbot is a computer program that enables humans to interact with technology by simulating and processing a conversation on a basic level. Using a variety of written and spoken input methods, humans can interact with digital devices in the same way they would communicate with human agents.
These tools are designed to automatically respond to questions and messages by drawing on information stored in a database or learning over time with artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms.
The functionality and intelligence of chatbot technology will vary depending on the software’s complexity and the environment it’s used in. A chatbot can be a rudimentary program that responds to simple questions with short responses, or a more complex digital assistant learning and evolves as it collects and processes information.
Chatbots have primarily been used in customer service to speed up support interactions; however, their uses are rapidly expanding. Nowadays, chatbots are used by small businesses and enterprises to provide enhanced customer experience and create a more efficient work environment.
They’re so prevalent in the digital business environment that they’ve come to be known by many names including virtual assistants, digital assistants, virtual agents, conversational agents and more.
Some chatbots are more intelligent than others. While a basic bot might be used to answer standard questions or carry out transactions, advanced conversational AI chatbots can deliver sophisticated support and enhanced capabilities to allow enterprises to deliver a customer experience like no other.

How do chatbots work?
Chatbot technology is often driven by AI, natural language processing, and machine learning. An ideal chatbot should respond to all types of requests and do so independently of a human agent. But how exactly does this work?
On a basic level, a bot works by analysing text or voice data input, considering the most appropriate response, and delivering it back to the user via a chat interface. Chatbot technology can work in several major chat messaging products (Facebook Messenger, Slack, Telegram, Whatsapp, etc.) and an independent platform.
There are two main types of chatbot: rules-based chatbots and machine learning chatbots (AI bots).
Rules-based chatbots function, as the name suggests, based on a set of rules. This is a less complex type of chatbot, as it’s only designed to respond to specific commands drawing on answers stored in a database. Essentially, a rules-based bot is only as smart as the data set it can draw on.
On the other hand, AI chatbots function using machine learning and are programmed to understand natural language, rather than just commands. This means they can understand more nuanced speech. They also grow ‘smarter’ as they converse with people, learning what questions may be asked and expected responses.
In the next section, we’ll look at how each type of bot functions in more detail.
Types of Chatbot Technology
Chatbot technology has become so advanced that understanding the various functions and capabilities of different bots can be challenging. As mentioned in the previous section, we can separate the two main types of chatbots into linguistic (rules-based) or machine learning (AI) categories.
It’s important to note that the chatbot space is constantly evolving and adapting to customer experience trends and to meet changing customer expectations and business needs.
1. Rule-Based Chatbots
Rules-based bots are task-oriented, single-purpose programs focused on performing a specific function—this type of chatbot functions by providing automated but conversational responses to user requests.
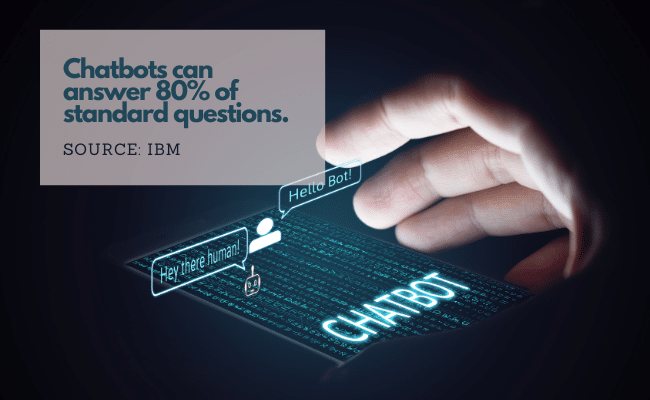
According to IBM, chatbots can answer 80% of standard questions. They can provide more robust and interactive FAQ responses, such as questions about business hours or simple transactional queries. They’re currently the most common type of chatbot. However, interactions with rules-based bots are more specific and structured than those with bots that use machine learning.
This type of task-oriented bot is capable of handling common questions that don’t involve many variables. Though they use NLP to facilitate conversational interactions, they offer limited capabilities and use if/then logic to converse with customers and determine their next steps. For this reason, they can be leveraged by businesses to provide consistent customer service.
Most of us have interacted with this type of bot in the past, on social media or a business’s eCommerce website, whether we were aware of it or not. This kind of bot can be a valuable asset to a business looking to enhance customer support teams’ control and flexibility and increase human agent productivity by handling common requests.
2. AI (Conversational) Chatbots
Here’s where things get more interesting.
Chatbots that use AI and machine learning are sometimes referred to as virtual or digital assistants. They use sophisticated technology to provide more interactive, personalised, and data-driven experiences than rules-based bots.
When a customer interacts with an AI chatbot, they’ll have a more conversational experience than if they were to interact with a rules-based one. As the bot responds to data patterns and AI algorithms, they become more contextually aware as time goes on and leverage natural language understanding to replicate human behaviour.
This bot can apply predictive intelligence and advanced analytics to personalise interactions based on user profiles and their past behaviour. They can even learn the user’s preferences, initiate conversations, and anticipate the user’s needs. Some examples of advanced AI bots that you might even have around your home include Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri.
It’s taken a lot of time and effort for chatbots to arrive at where they are now. Programming a machine to understand a human isn’t an easy task. Human speech is nuanced, complicated, and extremely challenging to replicate artificially.
Conversational bots use several key natural language principles to understand and replicate human speech and behaviour. Let’s take a closer look at how this works.
-
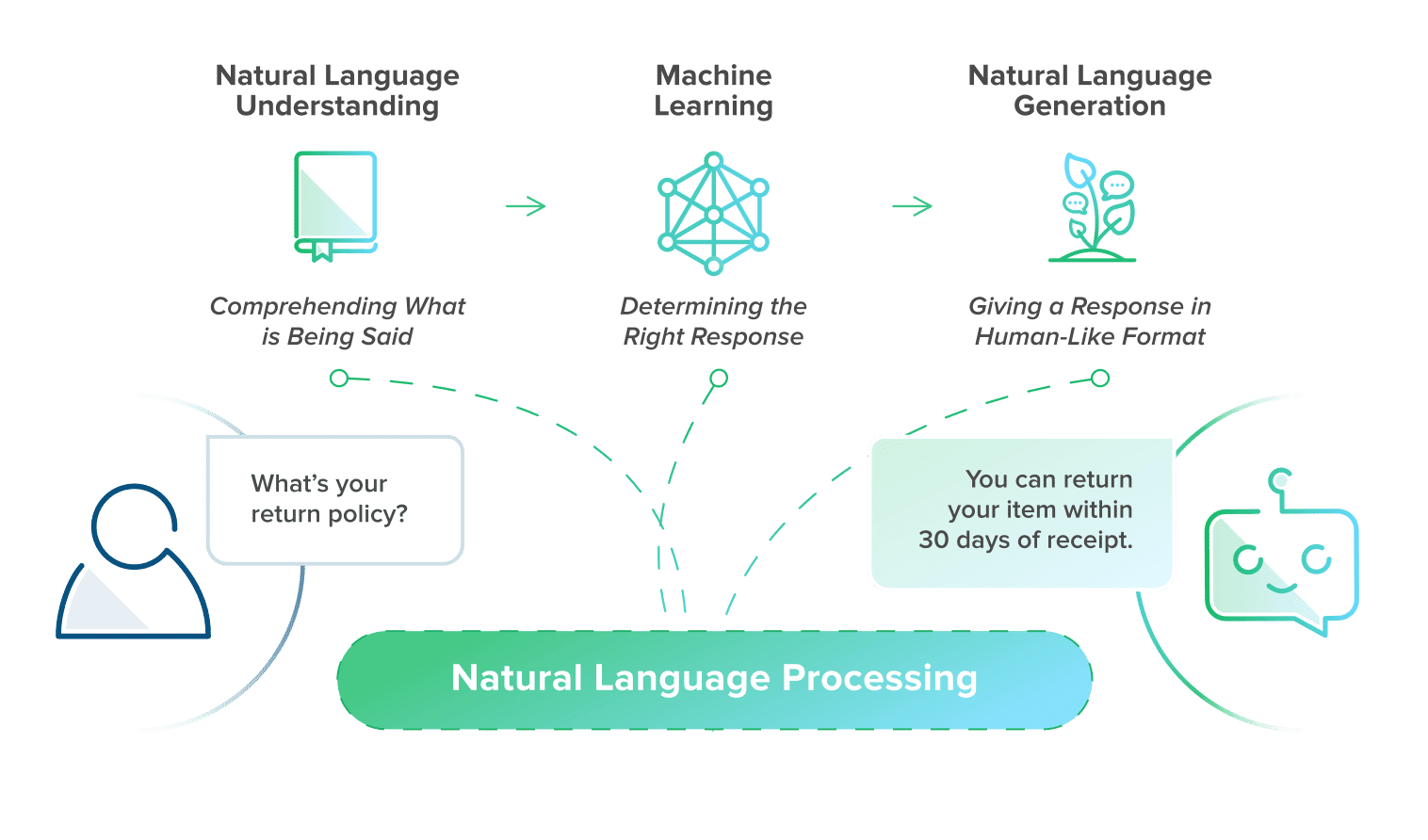
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP refers to the process of breaking down sentence structure, analysing broken grammar, understanding idioms and other elements of speech, and recognising patterns to determine what the user is saying. In everyday speech, we often have various ways to say the same thing; NLP allows bots to understand this and respond appropriately.
There are two main processes involved in natural language processing: understanding and generating.
-
Natural language understanding (NLU)
NLU allows the bot to understand user intent by using language features like lexicons, synonyms, and more complex themes. Used along with rules and algorithms, NLU identifies parts of speech to understand what the user is attempting to do.
-
Natural language generation (NLG)
Once the bot knows what the user is trying to do, they need to translate their answer from machine code into human language. NLG allows bots to deliver personalised responses beyond scripted ones (the kind used by rules-based bots). With NLG, the chatbot can create a response based on autonomous deep learning.
Source: Bold360
Using NLU and NLG, AI chatbots can engage in advanced dialogues with users and deliver realistic, nuanced responses that mirror human speech.
What does an AI chatbot do?
An AI chatbot can not only answer a customer’s questions within a dialogue box; they’re also capable of carrying out several different tasks.
For instance, it could fill out a form, recommend a product or service, upsell, or even book an appointment for a customer. Moreover, AI chatbot applications can be integrated with third-party or backend software systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) or customer relationship management (CRM) to complete other complex tasks.
The goal of AI chatbots is to provide the most human-like interaction possible. Despite this, 40% of people still don’t care whether a chatbot or a real human helps them – as long as they’re getting the help they need!
It’s clear that the key to successful customer engagement is understanding the customer’s request and catering to their needs with a personalised and accurate response, regardless of where it comes from.
3. Hybrid Chatbots
A hybrid model provides the best of both worlds.
With a hybrid approach, users can benefit from the features of rules-based chatbots and machine learning bots. They allow for conversational systems, a transparent operating system, and consistent bot personality. Simultaneously, they use machine learning to facilitate smarter and more complex interactions by utilising data and AI algorithms.
By taking a hybrid approach, businesses can avoid the limitations of using one kind of system and enjoy improved flexibility and speed of development to boost the customer experience.
What is an AI chatbot platform?
Marketers and development teams use an AI chatbot platform to create and maintain chatbots. It simplifies the development of AI chatbot systems by allowing enterprises to efficiently build, deploy, and maintain conversational systems for various messaging platforms.
These platforms (we can think of them as toolkits) should feature all the tools a developer needs to build a conversational system. From data mining tools to NLP tools, an AI chatbot platform provides all the necessary features to create, maintain, and analyse the system.
The key features of an AI chatbot platform include:
- A graphic user interface (GUI): Allows developers and business users to view the system. This allows developers to visualise the system from a customer perspective and adjust accordingly.
- Data analytics: Insights and data gathered from a chatbot application feedback into the system in real-time to provide more personalised responses.
- Flexible connector, software development kit (SDK): A collection of tools allowing developers to compile and debug code.
- An application programming interface (API) features: This allows businesses to effectively scale chatbot applications to suit their needs, and integrate them into various platforms such as their website or Facebook page.
There are countless enterprise chatbot platforms on the market, so deciding which one is right for your business can be challenging. Enterprises should decide what functionality they desire from a chatbot application before investing.
Chatbot Limitations
Chatbots are used by businesses to increase customer engagement, enhance the customer experience, and automate business processes. However, they often don’t live up to their potential due to the restrictive technology that makes them function.
Rules-based chatbots are the type most frequently used by businesses to assist their customer service departments and operations. This kind of bot isn’t capable of facilitating rich, conversational interactions necessary to keep users engaged and satisfied.
This is problematic as it limits the interaction potential and the bot’s ability to assist the customer. For instance, it can’t guide users back to the subject being discussed, ask qualifying questions, or deal with issues once they reach a certain level of complexity. Without the ability to escalate to a human agent, this can lead to customers leaving in frustration.
Moreover, bots lack emotions. This can be incredibly challenging for customers as they don’t get the same empathy and understanding from a real person. That being said, we now have AI bots capable of having a personality and can be taught empathetic and emotional responses based on certain messages.
Gartner predicted that 40% of first-generation chatbot/virtual assistant applications launched in 2018 would have been abandoned by 2020. If this is the case, why aren’t all businesses acquiring advanced machine learning chatbots capable of creating deeper, humanlike interactions?
There are several reasons. AI bots require huge amounts of training data and highly skilled professionals to operate and maintain their systems. The idea that a machine learning bot is a sentient being is simply not true. Moreover, they operate as a black box, meaning that professionals can find it difficult to intervene if something goes awry with the bot model.
The major limitations of machine learning bots are as follows:
- Collecting and categorising training data required to build an AI chatbot application is costly and time-consuming.
- They require ongoing review, consistent maintenance, and optimisation of their knowledge base. Tracking every bot conversation and analysing the interactions can be difficult or utterly impossible.
- They run the risk of not understanding the customer’s behaviour or request. Pure machine learning systems can also have inconsistent personalities, as they’re built on fragments of conversations and other resources.
- The regulations and legislation protecting data can pose challenges for storing, retrieving and deleting data that chatbots collect and require to function.
Chatbots vs Live Chat
According to a study by Econsultancy, 79% of consumers prefer live chat functions because they don’t have to wait in hold lines and have their questions answered immediately.
Live chat refers to an online communication app that enables website visitors to chat with customer service reps in real-time. It’s a good alternative to phone calls and emails, as all the customer has to do is type a message into the dialogue box and click send.
When implemented well, live chat software is a fantastic tool that enables customers to contact businesses via their website or social media without waiting in a phone queue.
However, live chat doesn’t always guarantee an immediate response. If there is no agent available to answer a request, customers will be prompted to leave an email address or voicemail for someone to get back to them. If live chat responses are delayed, or worse – non-existent, customers can be left frustrated or put off a business altogether.
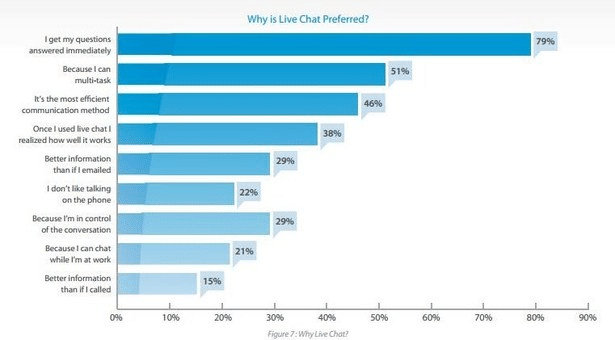
Source: Econsultancy
For this reason, chatbots offer some key advantages over live chat contact centre agents. These include:
- 24/7 support: Chatbots are available whenever your customers need across many different channels. This means customers can access support out of hours, or when no agents are available to take their call. Moreover, conversations can be seamlessly transferred between channels. A customer might start the interaction on a desktop and continue it later via a mobile app.
- Faster responses: AI chatbots are designed to efficiently understand and respond to customer requests within seconds, which means they can drastically reduce wait time and IVR technology limitations. While agents might need time to sift through a knowledge base for answers to standard queries, chatbots draw their responses near-instantly. One company found that their chatbots responded to support enquiries within 5 seconds, where their live service agents took on average 51 seconds.
- Accuracy: AI bots have a high level of understanding, meaning they can solve customer support queries quickly and accurately. This results in improved first call resolution rate and a higher chance of interacting with the chatbot again.
- Scalability: Chatbots can handle multiple customers simultaneously and to the same high standard of support quality.
- Compliancy: Chatbots are programmed to be compliant with data laws and industry regulations. Moreover, they allow for improved transparency and accountability, as all conversations are trackable.
Despite this, sometimes, a problem will require creative-problem solving skills or human judgement to resolve. When overly complex situations arise, it’s crucial that the bot can seamlessly transfer the query and all the information that arose during the conversation to a live agent.
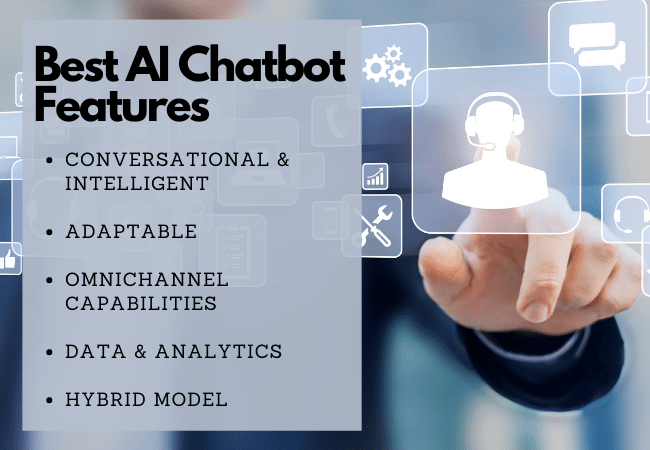
Best AI Chatbot Features
There are some essential features that a chatbot online application should offer. It should be:
-
Conversational and intelligent
The bot must understand the user’s intent (even if sentences are complex) and make intelligent exchanges of information. It should recognise and understand slang, idiots, and colloquial speech. Engaging and intelligent conversations allow chatbots to improve the customer’s experience effectively.
Moreover, essential bot memory enables it to reuse information to provide contextually personalised support and the most humanlike interaction possible. Enterprises need chatbot platforms that facilitate all of this and provide multi-language support.
-
Adaptable
Your chatbot represents your business, so it needs to offer customisable options to suit your business objectives and customers’ needs. The chatbot solution should be easily implemented, mould to your business, and adapt quickly to meet dynamic business needs.
-
Omnichannel capabilities
The chatbot application you choose should feature omnichannel capabilities that support users as they switch between devices and online apps throughout the day. Meet customers where they are, and you’ll see better engagement and customer satisfaction rates. This means ensuring the bot supports web and mobile apps and diverse operating systems (Android, iOS, Mac, Windows, Linux).
The user should seamlessly switch between channels (e.g. Facebook Messenger, website live chat) without losing the thread of conversation.
-
Data & Analytics
A bot that provides in-depth customer data and analytics will allow businesses to tailor their products and services to meet customer expectations. Moreover, data extracted from client requests, responses, and other information enables the bot to provide personalised support.
Combined with other information like geolocation, interaction channel, and purchase history, this data can customise the immediate interaction and feedback into the machine learning algorithms, improving future conversations.
-
Hybrid model
As we mentioned before, purely rules-based or machine learning chatbot models have the limitations. Therefore, a hybrid approach that combines both models’ best features allows businesses to provide optimised customer service using data insights via a consistent bot personality that’s aligned with business objectives.
You can also combine chatbots with human agents, allowing the chatbot to provide immediate responses that agents can edit. This saves them typing everything from scratch and looking up relevant information, while still adding a personal touch.

The Value of AI Chatbots for Business
In today’s fast-paced world, customer support, marketing, and sales teams have a lot to juggle. Between staying on top of consumer expectations and constantly working to improve the customer experience, it’s surprising that the modern marketer has time to breathe!
Luckily, AI chatbots can automate business operations and improve the customer experience with personalised, accurate, and timely interactions. Users value chatbots because they offer speedy, intuitive, and convenient responses to their queries.
AI chatbots enable businesses to provide personalised customer engagement. In return, better engagement leads to valuable customer information that can be leveraged to understand customers better and grow as a business.
Key benefits of chatbots for businesses
Below are some of the key benefits of AI bots for businesses.
- Drive sales and revenue: AI chatbots guide customers through their buying journey, driving conversion rates and boosting revenue. Moreover, intelligent bots can use contextual data to provide customers with advice and suggestions to upsell products and services.
- Reduce operational costs: Businesses can service more customers while reducing inbound call centre queries and improving first call resolution rates.
- Increase agent productivity: Chatbots can answer many calls, emails, SMS, and social media enquiries. They can be used to streamline workflows and free up agents to focus on more complex customer engagements of higher value.
- Increase customer engagement: Online communication is often more convenient for customers. Chatbots can provide new avenues for providing automated and personalised customer service to each customer, without making them wait.
- Allow businesses to understand better their customers: Customer data gleaned from bot interactions can be used to interpret customer behaviour and sentiment. This can be used to inform product and service development strategies.
- Drive product differentiation: With AI chatbots, businesses can deliver a frictionless customer experience that drives product differentiation with improved customer engagement, innovation, and efficient interactions.
- Combat customer churn: If your support team is swamped with high volumes of support requests, contact centre automation can prevent customers from becoming frustrated with long wait times or disorganised knowledge bases.
AI Chatbots for Customer Experience
Increasing engagement and providing personalised support is one of the main advantages of chatbots. Chatbots can transform customer service and elevate customer experience to build better relationships that result in loyal, happy customers.
Chatbots provide the right response every time. Moreover, with NLP, memory, and analytics, they can effectively customise the support to suit a particular user’s needs. They take the best aspects of live agent support (conversational and intelligent understanding) and machine learning technology (data, speed, and accuracy) for optimised support that ensures customers get the best response every time.
Implemented into a contact centre solution, chatbots are the ideal conduit for resolving customer service problems, providing general advice, and carrying out many common tasks.
Chatbot Examples, Use Cases, and Case Studies
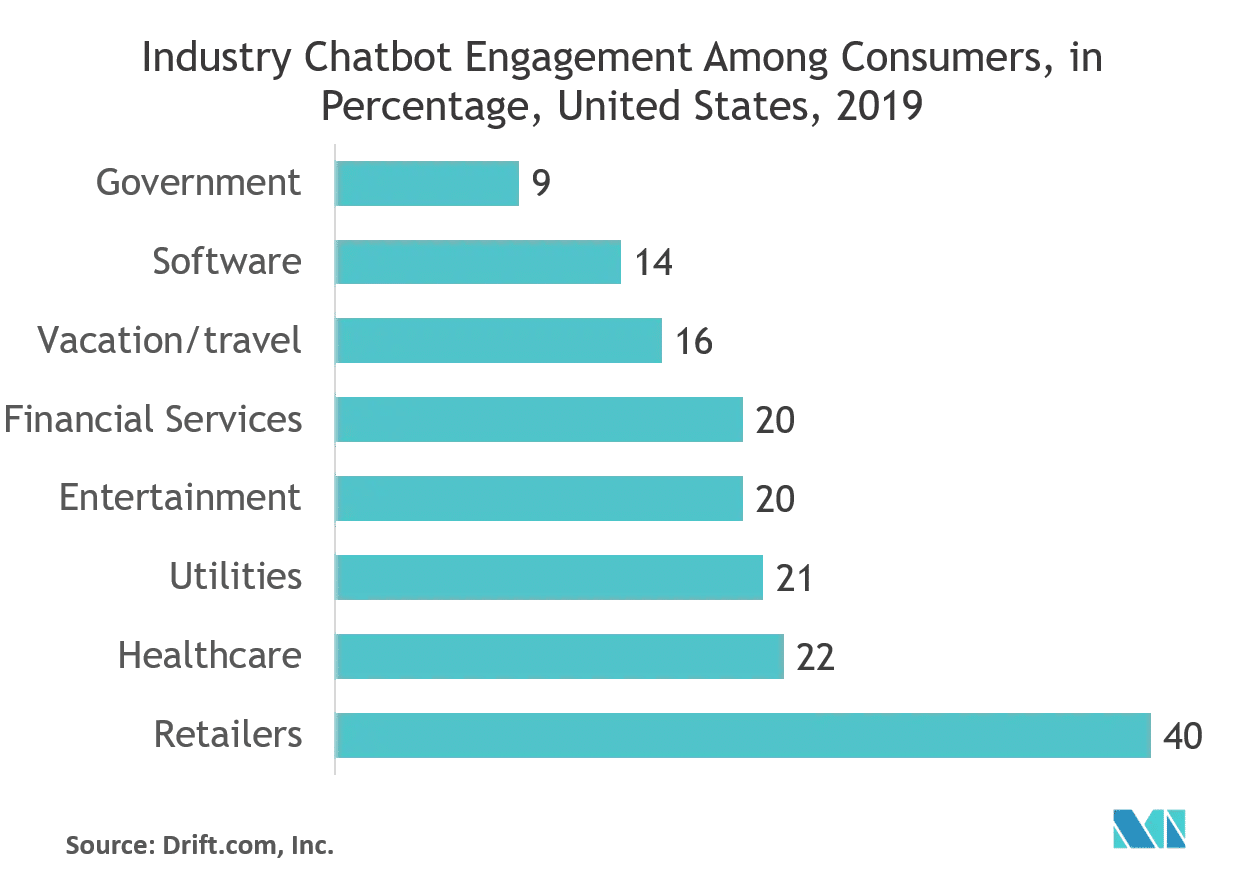
Source: Mordor Intelligence
Chatbots are employed across industries to facilitate customer service, improve sales processes, and increase marketing reach. Let’s take a look at how chatbots are deployed by businesses to improve the customer experience.
Chatbots in customer service
Chatbots can answer questions and handle support requests in the same way that a real person would.
Use cases
Whether it involves product information or shipping updates, customers can interact conveniently and timely on the channel of their choice. Healthcare industries can deploy them to help customers book appointments, by travel and tourism companies to make reservations or provide suggestions or telecommunications operators to resolve technical issues.
Other chatbot capabilities include finding products, checking inventory, processing returns and exchanges, confirming orders, and tracking shipments. Most importantly, they can improve the overall customer experience by providing streamlined, personalised, and accurate support.
Customer service chatbot case study: Amtrak
Popular American railroad company Amtrak received over 4.6 million visitors to their website in 2020. Their chatbot, Julie, enables travellers to book trips by typing where they want to travel into the chat box interface. Designed to operate like Amtrak’s best customer service reps, according to Next IT, Julie has:
- Answered over 5 million questions
- Generated 30% more revenue per booking
- Saved Amtrak $1 million in customer service email costs
- Delivered an 8x return on investment
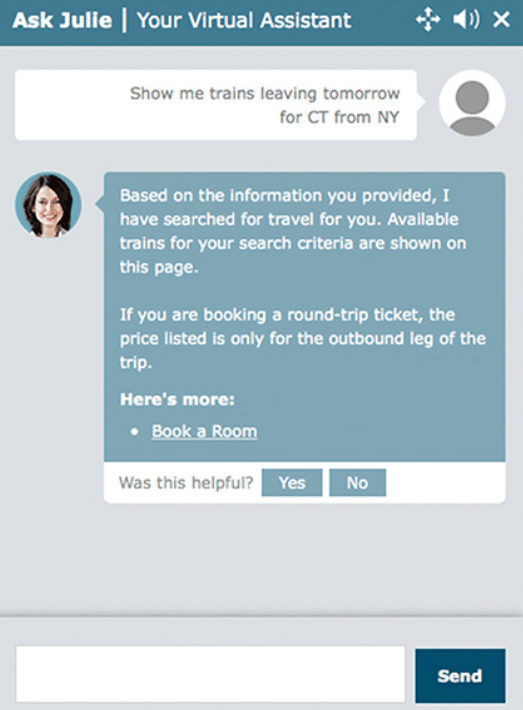
Source: Next It
Chatbots in sales & marketing
Chatbots have many applications in business sales and marketing departments. From front line sales to facilitating email collections and marketing campaigns, chatbots can improve the overall customer service experience and enhance employee productivity.
Chatbot use cases in sales & marketing
They can enhance the shopping journey by providing real-time support on a business’s eCommerce website. A bot can provide personalised shopping advice that can boost conversions by assisting customers in their journey through the sales funnel.
Bots can also be used to collect and analyse information gleaned from interactions with customers. This allows them to anticipate user needs and behaviours to better target marketing messages and campaigns. Moreover, a bot can be programmed to subscribe to email newsletters and other forms of marketing content.
Additionally, bots can be used to implement a systemised follow-up system to encourage customers to take further actions with your business. They can also reduce cart abandonment by pushing product information or suggesting alternative payment methods when one fails.
Businesses with their own chatbot to facilitate sales and marketing processes will see increased sales, build better customer relationships, and boost RoI.
Sales & marketing chatbot case study: Sephora
Beauty brand giant Sephora has three bots available to automate online customer interactions:
- Sephora Reservation Assistant (Facebook Messenger)
- Sephora Virtual Assist (Facebook Messenger)
- Sephora’s Kik bot
Combined, these bots can make in-store reservations for customers, answer questions, and provide beauty advice and tips. What’s more, customers can also find products matching those used by their favourite celebrities by scanning an image or trying on products by uploading a photo of their face.
With their chatbots, Sephora delivered targeted marketing to guide customers with tutorials, product description, and promotions, while boosting the brand’s online presence with quirky and engaging bot conversations.
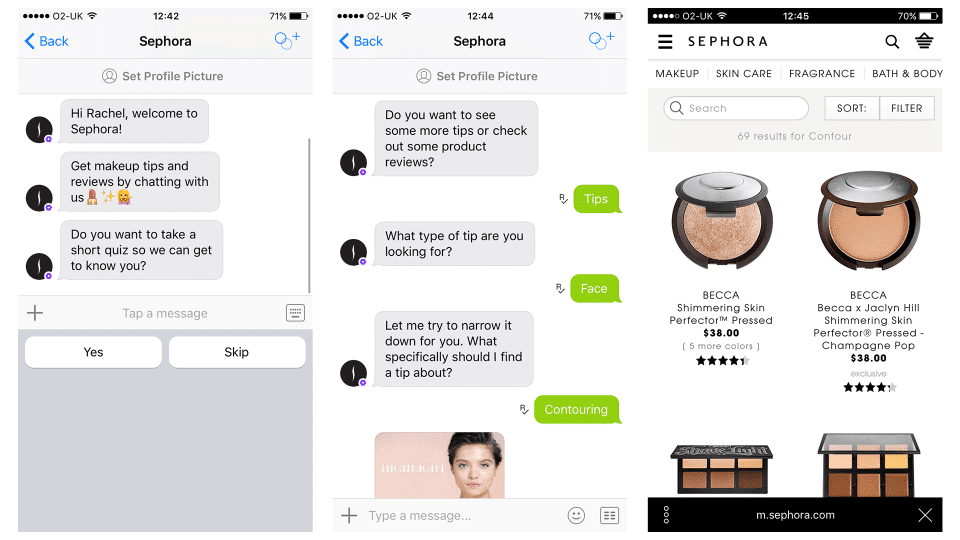
Source: LinkedIn
Chatbot Statistics (New Data – 2020 & Beyond)
Market growth
Mordor Intelligence’s report found that the chatbot market was worth 17.17 billion in 2019, and is projected to reach USD 102.29 billion by 2025, registering a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 34.75% over the period. The report found that the fastest growing regional market for chatbots is the Asia Pacific, with North America retaining the largest market size globally.
Reports and Data found that the market for chatbots in the Asia Pacific has a growth rate CAGR of 9%. North America followed this at 31.2 % CAGR and Europe with a 30.4% CAGR. It was also found that chatbots in the customer service segment are expected to be the fastest-growing market segment between 2019-2026, with a CAGR of 31.6%.
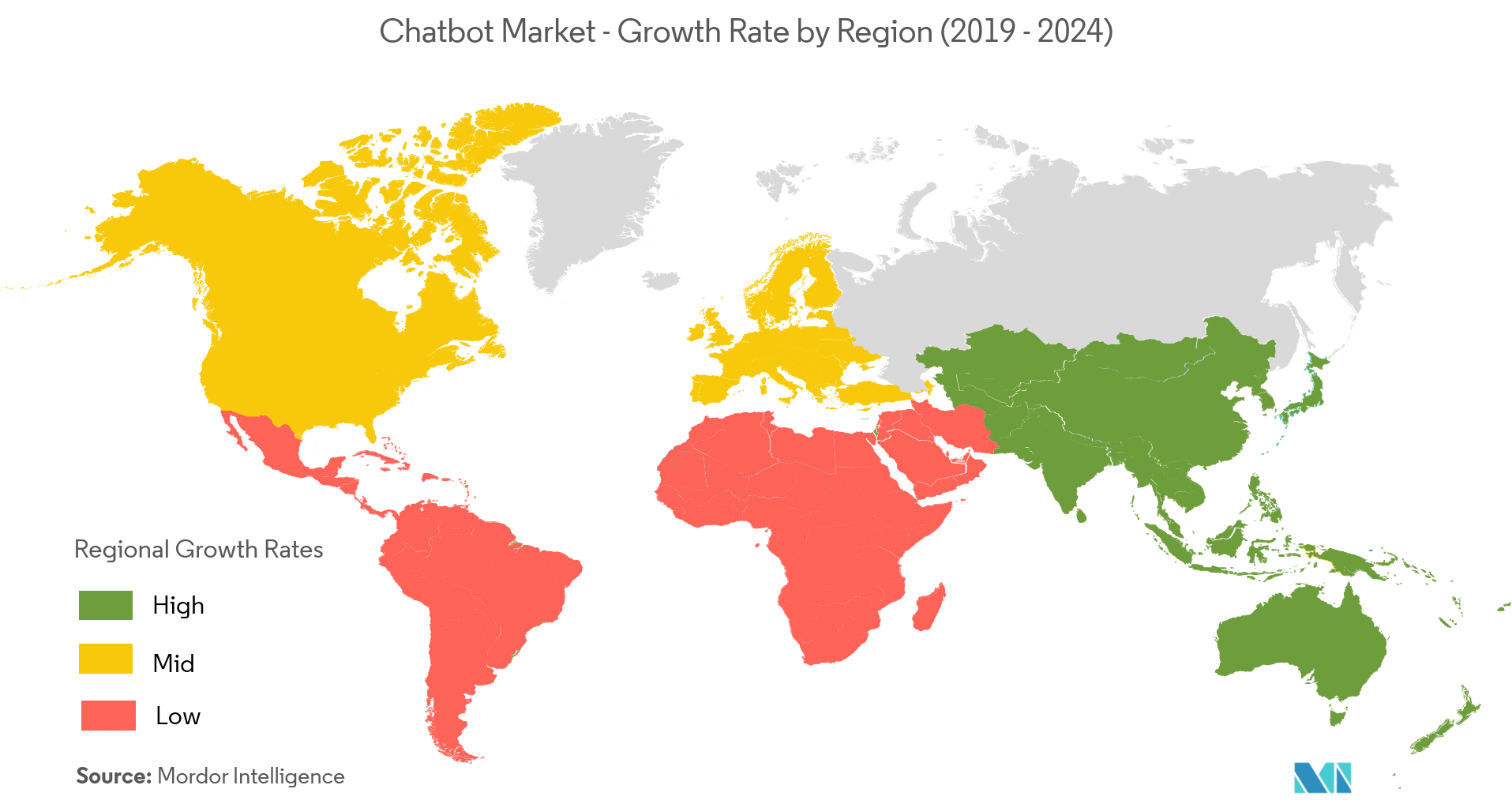
Source: Mordor Intelligence
This growth of the AI chatbot segment is fuelled by increasing demand for automated solutions that offer real-time customer insights and omnichannel deployment and rapid advancements in AI and machine learning technologies. Gartner predicts that by 2021, more than 50% of enterprises will spend more per year on chatbot platforms than traditional mobile app development.
From chatbots to smart speakers, virtual assistants are becoming more prevalent for a variety of use cases across a diverse range of industries. It’s estimated that by 2022 70% of white-collar workers will undertake daily interactions with conversational platforms.
Chatbot usage and engagement statistics in 2020 & beyond
Currently, 74% of consumers report they use virtual assistants for researching or buying products and services. Moreover, 70% of millennials who have used chatbots report having had positive experiences. According to Salesforce, 77% of customers agree that chatbots will transform their customer experience expectations during the next five years.
Below are some important predictions about chatbot usage and engagement for the year 2021 and beyond.
- By 2021, one in six customer service interactions globally will be handled by AI. (Gartner)
- Bank systems can automate up to 90% of customer interactions using chatbots by 2022. (Juniper Research)
- 5 billion hours of projected time savings are predicted for businesses and consumers due to chatbots by 2023. (Juniper Research)
- By 2023, chatbots are predicted to save banking, healthcare, and retail sectors up to $11 billion annually. (Juniper Research)
- By 2023, the number of people with disabilities employed will triple due to AI and emerging technologies increasing accessibility. (Gartner)
- By 2024, AI will become the new user interface by redefining user experiences where over 50% of user touches will be augmented by computer vision, speech, natural language and AR/VR (IDC).
- By 2025, customer service organisations that embed AI in their multichannel customer engagement platform will elevate operational efficiency by 25% (Gartner).
- By 2025, AI will power 95% of all customer interactions, including live telephone and online conversations, and will be so human-like that customers won’t differentiate between human agents and machines (Finance Digest).
Chatbots and COVID-19
2020 has been an unpredictable year for everyone. The global Covid-19 pandemic highlighted areas of weakness within enterprises that weren’t prepared to face a worldwide shut down and didn’t have an effective contingency plane.
Countries worldwide were subjected to quarantines, SMBs, and enterprises had to ensure business continuity in the face of a global crisis. For some, it was impossible. For others, it meant rapidly switching to remote working, transforming business operations, and reimagining customer service, supply chains, and other business operations to align with reductions in in-person interactions.
As consumers turned to digital channels to communicate, seek help, and carry out transactions, businesses had to adapt quickly to ensure operational continuity met customer expectations. Contact centres were overwhelmed with calls from worried customers, and online retail environments overwhelmed with increasing demand for services via digital channels.
As a result of this, AI chatbots have been increasingly deployed by businesses and organisations to manage customer demand and reduce the burden for customer service agents. Their ability to reduce long-wait times with swift and personalised automated responses take businesses to new levels, maintaining continuity and enhancing the customer journey. Even simple, rules-based bots can have a huge impact, answering questions about changes to opening times, return policies or delivery expectations.
AI chatbots have helped businesses and organisations to share information, communicate with customers, and avoid the challenges that arose during the spread of Covid-19. Along with their application in customer service and online retail environments, chatbots have also been invaluable for the healthcare industry. For example, WHO launched a multi-language Facebook Messenger bot that provided instant and verified information about Covid-19 to Facebook users to combat the spread of fake news and provide advice and support during a crisis.

Source: https://www.ringcentral.com/gb/en/blog/public-sector-property-post-covid/#ring-uk
Types of Chatbot Technology
It might seem like technology has reached its peak. Hollywood films might have us believe that artificial intelligence and machines that can act and converse like humans signal the world’s end as we know it.
The common misconception about AI is that it will take away our jobs, humanity, and eventually replace us altogether. However, when viewed as a tool to enhance, rather than replace, human capabilities, it’s clear AI isn’t a technology to be scared of. So, what does the future of AI technology hold when it comes to chatbots?
The chatbot market is maturing quickly. Chatbots and AI tools will continue to enhance human abilities by automating time-consuming processes or answering common requests to free up human agents to focus on strategy and more complex tasks.
As chatbots mature and become capable of having more sophisticated conversations, customers and enterprises can benefit from a transformative communication experience that’s swift and accurate. Moreover, NLP and machine learning developments will generate more intricate AI algorithms to allow businesses to create more personalised, unique customer experiences for their clients.
Combined with developments in 5G technology and customer service trends, chatbots are likely to develop new features and improve old ones with faster recommendations and predictions, access to in-chat video conferencing, and more nuanced conversational responses.
To remain competitive in an age of digital transformation, businesses must adapt to growing technology and customers’ ever-changing demands.
Originally published Aug 19, 2021, updated Apr 10, 2023